Views: 1000 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-28 Origin: Site









As people age, the quality and quantity of muscle tissue in the human body gradually decrease. This phenomenon is known as sarcopenia—the functional decline of skeletal muscle during the aging process. Sarcopenia directly leads to a decrease in muscle strength and function, thereby affecting mobility; in severe cases, it may even result in the loss of physical independence and disability.
Mitochondrial dysfunction: Mitochondria are the "energy production centers" within cells, responsible for generating the energy molecule ATP (adenosine triphosphate) required for cellular activities. When mitochondrial function is impaired, it causes insufficient energy supply to muscle cells, disrupting their normal functions and metabolic processes, and accelerating muscle loss.
Decline in NAD+ levels: NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is an essential intracellular coenzyme that regulates energy metabolism and redox reactions. With aging, cellular NAD+ levels decrease significantly. This decline disrupts intracellular redox balance, intensifies oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, and ultimately impairs muscle cell function and survival.
Basic properties: Trigonelline is a natural alkaloid present in plants and animals, widely found in common foods such as coffee, fenugreek, and radish.
Clinical correlation: Early studies revealed that sarcopenia patients have relatively low circulating concentrations of trigonelline; as muscle mass decreases, serum trigonelline levels drop further. Importantly, trigonelline is positively correlated with muscle strength and mitochondrial energy production in skeletal muscle, and its serum level is also associated with skeletal muscle NAD+ levels.

4.1 Trigonelline acts as a true NAD+ precursor:
Structurally, trigonelline is the N-methylated form of nicotinic acid (NA), with a structure similar to NA.
Isotope labeling experiments in mice showed that trigonelline is directly incorporated into NAD+ in cells and tissues, confirming its role as a genuine NAD+ precursor.
4.2 Superior stability compared to other NAD+ precursors:
In human skeletal muscle cells, trigonelline and nicotinamide (NAM) increase NAD+ levels by ~50% (while nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) increase levels by ~2x). However, trigonelline is highly stable in serum, whereas NR and NMN rapidly disappear within hours after conversion to NAM.
4.3 Mechanism of NAD+ synthesis:
Both in vitro and in vivo results demonstrate that trigonelline is metabolized via the Preiss-Handler pathway (dependent on nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase, NAPRT) and promotes NAD+ synthesis through direct and indirect mechanisms.
Prolongs nematode lifespan;
Increases NAD+ levels in aged nematodes;
Enhances mitochondrial activity;
Improves age-related muscle atrophy.
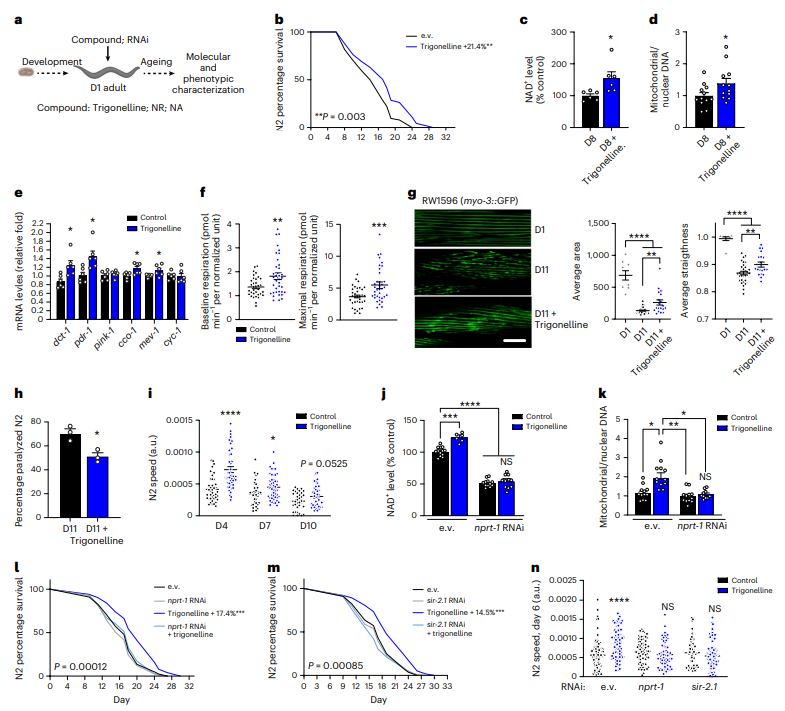
Enhances mitochondrial activity and muscle function;
Prevents fatigue during aging.
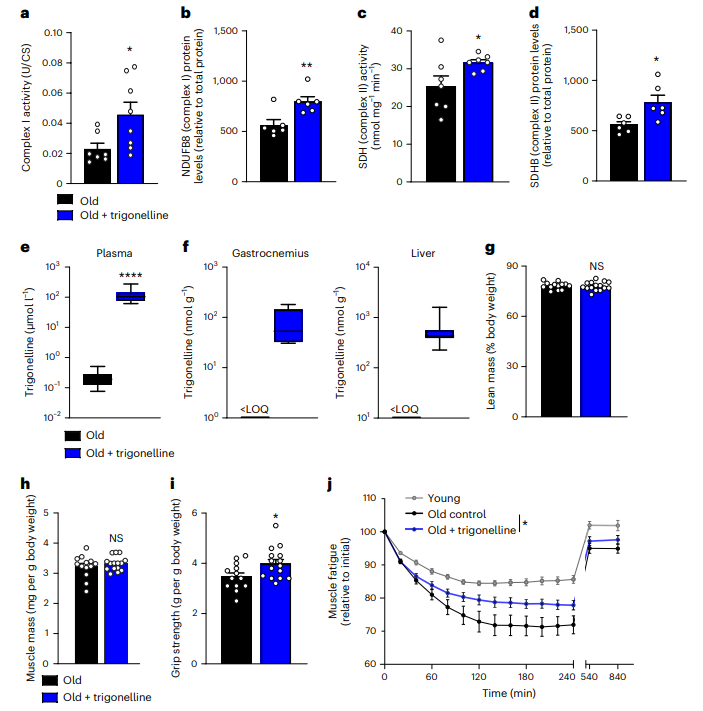
Note: The study also identified sesamin (another compound) as an NAD+ precursor, which similarly enhances mitochondrial activity and muscle function in mice. Dietary supplementation of sesamin benefits mitochondrial function, muscle health, and mobility in aging.
L-tryptophan;
Vitamin B3 and its derivatives: nicotinic acid (NA), nicotinamide (NAM), nicotinamide riboside (NR), and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).
Important Reminder:All content in this article is for general reference only and is provided solely to offer information support for practitioners in the nutrition and health industry. Descriptions related to efficacy are supported by corresponding data, but they do not represent claims or guidance for consumers. Content related to health, medical care, and technological applications is for reference only. For medical matters, please consult professional medical institutions and follow medical advice. This article does not provide any medical recommendations.